How to validate your product idea?

The chance of developing a successful product varies depending on different criteria such as the domain, market conditions, the quality of the product idea, execution, timing, and competition. Unfortunately, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer to this phenomenon. However, research and statistics can provide some insights into the likelihood of success.

Some interesting figures: According to the source, the Startup Failure Rate is currently up to 90%. 10% of the newly launched startups witnessed failure within its first year. 34% of small businesses that are unsuccessful are due to poor product-market fit. The success rate of startups is only 10% to 20% in the long run. 45% of startups are unable to survive the fifth year.
Yes, we know. Sounds not promising. However, the desired outcome is achievable if we focus on factors contributing to the success of a product, which include thorough market research, validation of the product idea, understanding customer needs, effective marketing, robust custom software development, testing processes, and agile adaptation to feedback, etc.
Here, you can find the info on how to validate a product idea, so your big thing is worth the effort when released.
Turn your product idea into your big thing with our validation services
Why is it important not to ignore product validation?
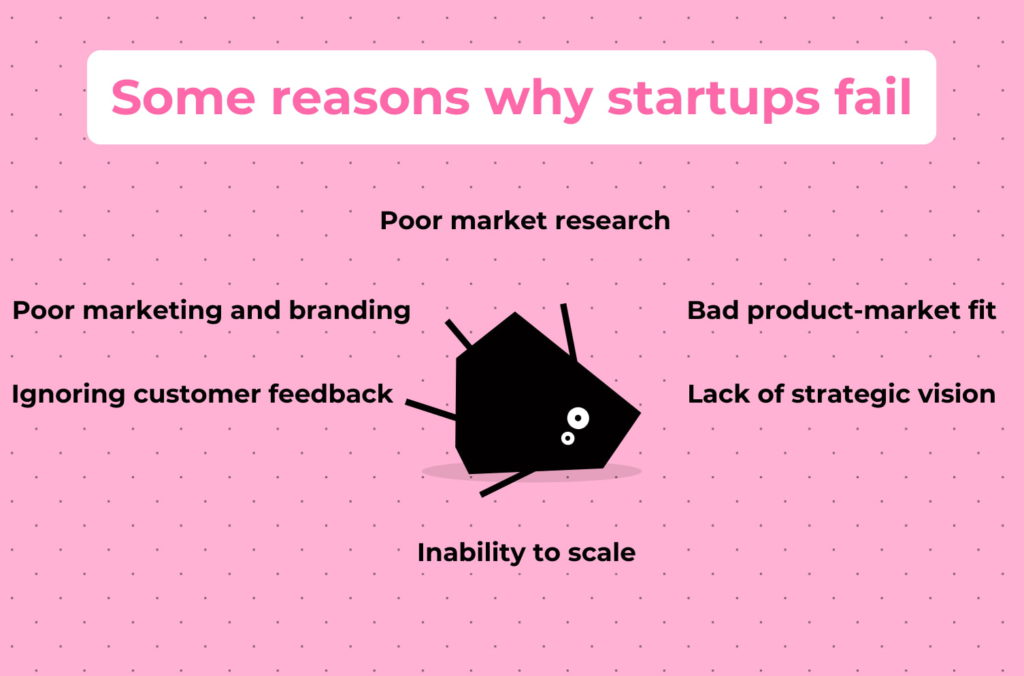
Sometimes it is helpful to push off from the opposite. Let’s see the main reasons why startups fail so we can make appropriate conclusions and efforts.
Poor market research: Without thorough market research, startups risk entering markets where demand is low, competition is fierce, or the target audience is poorly understood. This lack of understanding can result in misaligned product offerings, ineffective marketing, or failure to capture market share.
Bad product-market fit: Even if there is demand for a product or service, the inability to achieve a strong product-market fit can lead to failure. Startups may misjudge the needs or preferences of their target audience, resulting in a mismatch between what they offer and what customers want.
Lack of strategic vision: Startups may fail due to a lack of clear long-term vision or direction. Without a well-defined strategy, including goals, objectives, and a roadmap for growth, startups can struggle to make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and navigate challenges.
Inability to scale: Scaling a startup requires efficient processes, infrastructure, and resources. Startups may falter if they are unable to scale their operations to meet increasing demand or if they scale too quickly without adequate preparation.
Ignoring customer feedback: Ignoring or dismissing feedback from customers can be detrimental to a startup’s success. Customer insights are invaluable for refining the product, identifying opportunities for improvement, and staying aligned with market needs.
Poor marketing and branding: Even with a great product, startups can have problems if they fail to effectively market and promote their offerings. Inadequate branding, marketing strategies, or messaging can make it difficult to attract attention and build a loyal customer base.
Idea validation
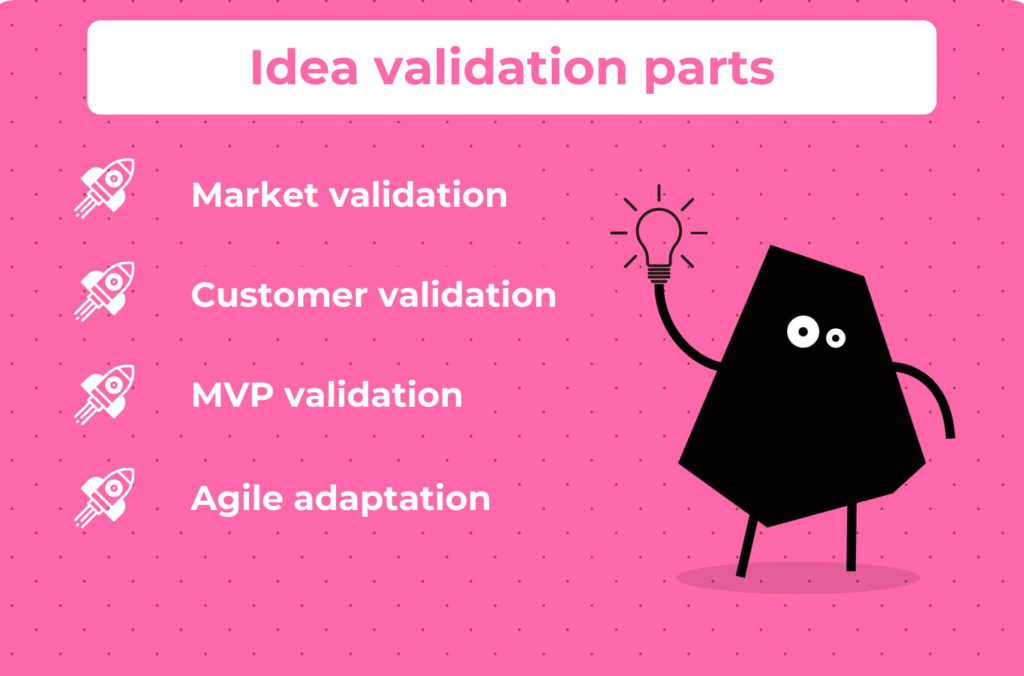
To avoid these mistakes, we start with idea validation. We bet you’ve heard that necessity is the mother of invention. It is required to figure out whether there is a need for such a product. With startup idea validation, you embark on a journey of discovery, seeking to understand not only the pain points of your target audience but also their willingness to embrace your proposed solution.
Startup idea validation
To ensure a future product meets real-world needs and resonates with your target customers, we need to make the validation process as deep as possible, so we do not miss anything.
Define assumptions: Start by identifying the key assumptions underlying your startup idea. These assumptions may relate to market demand, customer behavior, competitive landscape, or technological feasibility. Clearly articulate each assumption and the rationale behind it to guide your validation efforts.
Design validation experiments: Develop experiments to validate each assumption systematically. These experiments may take various forms, such as surveys, interviews, prototype testing, landing page experiments, or market research studies. Tailor your validation approach to the specific nature of each assumption and the available resources.
Define key metrics: Start by defining key metrics and performance indicators that align with your validation goals and objectives. These metrics may include customer acquisition metrics (e.g., number of sign-ups, conversion rates), engagement metrics (e.g., user interactions, feedback), market metrics (e.g., market size, competition analysis), and financial metrics (e.g., revenue projections, cost analysis).
Set benchmarks and targets: Establish benchmarks and targets for each key metric to provide a reference point for tracking progress and measuring success. Set realistic and achievable targets based on industry benchmarks, historical data, and market trends to gauge the effectiveness of your validation efforts and identify areas where improvements are needed.
Track experiment results: Keep track of the results of your validation experiments and tests to assess their impact on key metrics and outcomes. Document the methodology, findings, and conclusions of each experiment to ensure transparency and accountability. Analyze experiment results to identify patterns, trends, and correlations that can inform future validation efforts.
Regularly review and analyze data: Regularly review and analyze the data collected from various sources to assess your startup validation progress. Identify trends, patterns, and insights that indicate areas of strength or weakness in your validation efforts. Conduct regular review meetings or checkpoints to discuss progress, address challenges, and make data-driven decisions about the next steps.
Market validation
At this point, let’s focus on the core parts of product idea validation. One of them is market validation. Here, it is supposed to monitor industry trends, analyze competitor offerings, look for opportunities to differentiate your product, and identify potential gaps in the market that your product can address.
By staying informed about the competitive landscape, you can make informed decisions and position your product effectively. Plus, staying updated on consumer preferences and behaviors will benefit your product. This measure is directly related to the following validation part.
Customer validation
It refers to gathering feedback from potential customers through various channels, such as surveys, interviews, beta testing, or product demonstrations. Use this feedback to validate assumptions, identify pain points, refine your product concept, and, ultimately, enhance customer satisfaction.
This enables iterative refinement of the product based on real user insights, ensuring that it addresses genuine needs and resonates with the intended audience, thus enhancing its chances of success in the market.
MVP software development
Developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a crucial step in the validation process. An MVP is a simplified version of your product with the key features necessary to address the identified problem. Whether you are building an MVP for an IT healthcare project, fintech application, or real estate platform, MVP validation should be done without any doubts and regrets.
By building an MVP, you can test your assumptions, gather feedback, attract investors, and iterate based on real user experiences. Keep the MVP lean to minimize costs and time-to-market while still delivering value to early adopters.
MVP testing
Once you have built your MVP, it’s time to put it to the test. Launch a beta version of your product to a select group of users or offer it to a limited audience. Collect feedback from users regarding their experience, satisfaction level, and suggestions for improvement.
Pay close attention to user behavior, such as engagement metrics, conversion rates, and retention rates, to assess the viability of your product.
Agile adaptation
Based on test results and real user experiences, it is required to apply iterative refinement. It’s essential to remain agile and adaptable as you gather feedback, improve its features, usability, and value proposition, and iterate on your product.
Be open to making changes based on insights gained during the validation phase, even if it means pivoting or adjusting your initial concept.
Bonus tips on how to validate startup idea

Create a landing page and launch an ad: Design a simple landing page that highlights the key features and benefits of your product idea. Use compelling visuals, persuasive copywriting, and a clear call to action to encourage visitors to sign up or express interest. Track user engagement, such as click-through rates and conversion rates, to gauge interest and demand for your product.
Run social media polls: Leverage social media platforms to conduct polls or surveys to gather feedback from your target audience. Ask questions related to pain points, preferences, or willingness to try new solutions. Analyze the responses to identify trends, validate assumptions, and refine your product concept based on user input.
Host a virtual hackathon or ideation workshop: Organize a virtual hackathon or ideation workshop to engage with a diverse group of participants and generate innovative ideas for product validation. Facilitate brainstorming sessions, encourage participants to pitch their ideas, and vote on the most promising concepts. Use the workshop to validate ideas and identify potential collaborators or partners.
Offer pre-orders or early access: Create a sense of exclusivity and urgency by offering pre-orders or early access to your product idea. Launch a crowdfunding campaign or pre-sale event to gauge interest and incentivize early adopters to commit to your product. Monitor pre-order sales, conversion rates, and customer feedback to validate demand and refine your product strategy.
Partner with influencers or thought leaders: Collaborate with influencers or thought leaders in your industry to promote your product idea and gather feedback from their followers. Partner with individuals who have a strong online presence and credibility within your target market to reach a wider audience and validate your concept through their endorsement and insights.
Refresh old ideas: Revisit previous product concepts or ideas that were shelved or overlooked in the past. Consider how market conditions, technology trends, or consumer preferences may have changed since the idea was first conceived. Look for opportunities to update and revitalize old ideas with new features, innovations, or value propositions that address current market needs or trends.
Conclusion: startup idea validation is a fundamental step
Nobody will make it if they do not raise a question of how to validate a product idea. Remember that validation is an ongoing process, and staying agile and responsive to feedback is key to achieving product-market fit. With a validated product idea, you can proceed with confidence, knowing that you are addressing a genuine need in the market and providing value to your customers.