The role of digital transformation in the Insurance industry

Embrace digital transformation or be left behind. Speaking of the insurance industry, these words are not an exception. In the times defined by rapid technological advancement and shifting consumer preferences, digital transformation in the insurance industry encompasses the adoption of business intelligence, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and automation to enhance efficiency, improve customer experience, and drive innovation.
Some interesting figures: 81% of insurers cited AI as their leading strategic IT priority. By digitizing its insurance processes, insurers managed to reduce claims regulation costs by 20 to 30 percent. 48% of insurers say that innovation is helping to redefine their processes and products, emphasizing the role of technology in driving product development. 68% of insurance buyers want to conduct transactions online. Yet, less than 50% of insurers are able to digitally provide a product or service quote; fewer than 35% can process a transaction or sale digitally; and only 23% incorporate digital into the claims process.
These figures underscore the significance of digital transformation as a strategic ace for insurers looking to remain competitive and meet the evolving needs of today’s digital-savvy consumers. This article is about how digital transformation redefines the insurance domain and the key trends driving this evolution.
Integrate insurtech to get a boost and drive innovation
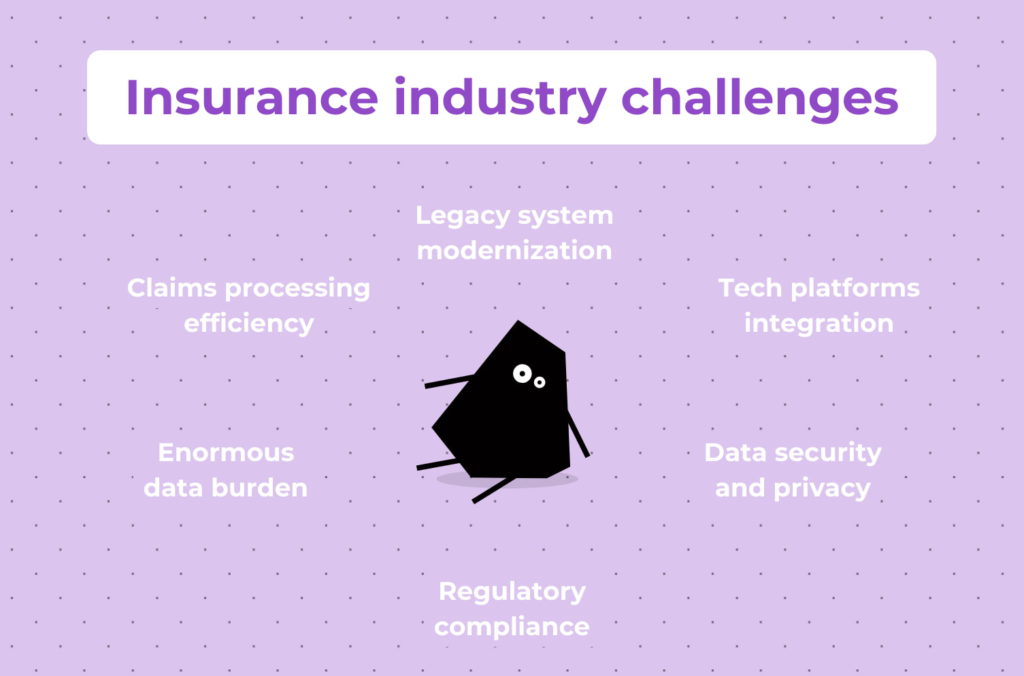
What insurance industry challenges do insurers face?
Digital technologies have revolutionized the insurance domain and forced it to adapt to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and competitive pressures. The technological change also helps insurers go through industry-related challenges. Let’s consider the latter first.
- Legacy system modernization: Many insurers rely on outdated software applications and manual processes that are inefficient and inflexible. These legacy systems hinder agility, innovation, and scalability, making it difficult for insurers to adapt to changing market dynamics and customer expectations.
- Integration of tech platforms: Insurers often have disparate systems and data silos that are not fully integrated, resulting in inefficiencies, data fragmentation, and information silos. The challenge impact is significant, as it impedes interaction and decision-making within insurance organizations and affects operational performance.
- Claims processing efficiency: Inefficient claims processing directly impacts customer satisfaction, operational costs, and profitability. Manual, paper-based processes can result in delays, errors, and inefficiencies, constraining insurers’ ability to provide timely and satisfactory service to policyholders while also increasing operational expenses.
- Enormous data burden: In the insurance industry, vast amounts of data are generated and collected from various sources, including policyholders, claims, underwriting, etc. Managing and analyzing this volume of data is tough since traditional data processing, data integration methods may struggle to handle the scale and complexity of the information.
- Data security and privacy: These are paramount concerns for insurers, given the sensitive nature of the data they collect and store. Insurers must comply with strict regulations governing the collection, storage, and use of customer data, such as GDPR and CCPA, and protect against cyber threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access.
- Regulatory compliance: The insurance industry is heavily regulated, with stringent requirements for product offerings, pricing, underwriting practices, and customer data protection. Compliance with evolving regulations adds complexity and operational costs for insurers, particularly in an era of increasing scrutiny and enforcement.
What are technology trends in the insurance industry and how can they address challenges?
Insurtech encompasses a diverse array of innovations across the insurance value chain. One of the key trends driving Insurtech is the use of data analytics and AI and ML to revolutionize underwriting and risk assessment. Insurers are leveraging big data and predictive analytics to gain deeper insights into customer behavior, assess risks more accurately, and develop personalized insurance products tailored to individual needs. Let’s look through them closer:
AI in the insurance industry
AI transformation is revolutionizing various aspects of the insurance industry, including underwriting, claims processing, risk assessment, and customer service. AI-driven claims processing systems can analyze claims data, identify patterns, and make decisions autonomously, reducing the need for manual intervention and speeding up the claims adjudication process.
This approach can streamline claims processing workflows by automating routine tasks such as claims intake, data extraction, and claims adjudication. Plus, Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms can parse and interpret unstructured claims documents, while image recognition technology can analyze images and documents for relevant information, enabling faster claims settlement.
Automation in the insurance industry
In addition to claims processing automation with technologies, the next thing shall be automated underwriting and customer service. Insurers can automate the underwriting process by analyzing vast amounts of data, including demographic information, claims history, and credit scores, to make faster and more informed underwriting decisions.
Automation tools such as chatbots and virtual assistants provide personalized assistance to policyholders, answering inquiries, guiding them through the insurance process, and resolving issues in real time. Automated customer service enhances the overall customer experience, reduces wait times, and enables insurers to deliver proactive support around the clock.
Data engineering in the insurance industry
Data engineering is a powerful tool to effectively handle enormous data, its processing, quality, governance, and even legacy systems. Overall, it ensures that data is collected, stored, processed, and analyzed efficiently. Let’s look at how it works:
- Data migration and cleansing: Cleaning and migrating data from legacy systems to modern data repositories or data lakes is essential for ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and accessibility. Data cleansing processes help identify and remove duplicate, outdated, or erroneous data, improving the quality and reliability of information used for decision-making.
- Data integration and management: involves integrating data from multiple sources, including internal systems, external databases, and third-party platforms, into a centralized data repository. Data engineers design and implement data pipelines and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes to ingest, cleanse, and transform data, ensuring its consistency.
- Real-time data processing: Data engineering enables real-time data processing by implementing stream processing architectures and event-driven workflows. Data engineers design and deploy data pipelines that ingest and process streaming data in real time, enabling insurers to detect and respond to events as they occur.
- Data quality and governance: Data engineering encompasses data quality assurance and governance practices to ensure that data is accurate, consistent, and compliant with regulatory requirements. Data engineers implement data quality checks, validation rules, and anomaly detection algorithms to identify and address data quality issues proactively.
Data analytics in the insurance industry
By analyzing vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, insurers can identify trends, detect fraud, and predict future claims with greater precision. By leveraging big data technologies such as distributed computing frameworks and parallel processing, insurers can handle massive datasets and perform complex analytics tasks in real-time or near-real-time.
Data analytics enables insurers to extract valuable insights from their data, identify patterns, uncover hidden correlations that can inform decision-making across various business functions, and ultimately refine raw data into dollars. Moreover, data analytics empowers insurers to leverage predictive modeling techniques to forecast future events and trends based on historical data and statistical analysis.
Cloud computing in the insurance industry
Moving to cloud-based solutions offers numerous benefits, including scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. Insurance companies can leverage cloud platforms to modernize their infrastructure, deploy new applications, and access the said advanced capabilities such as AI, ML, and big data analytics.
Insurance industry software solutions
These software solutions with a suite of features designed can fortify data protection measures and ensure adherence to regulatory standards. With advanced encryption protocols, access controls, and data anonymization techniques, insurance industry software solutions provide a fortified fortress for managing sensitive information such as policyholder data and financial records.
In addition to bolstering data security, software solutions for the insurance industry streamline regulatory compliance efforts across diverse jurisdictions and regulatory frameworks. Equipped with specialized compliance modules and configurable workflows, these solutions automate the process of regulatory reporting, documentation, and audit trail creation.
However, the capabilities of insurance industry software are not limited to addressing the said problems. It can be customized to meet any unique needs. Custom software development solutions always give results.

Conclusion: digital transformation in the insurance industry is not an option, it’s a necessity
The impact of digital transformation extends beyond operational improvements; from policy management to claims processing, it fundamentally reshapes the competitive landscape of the insurance industry.
Insurers that successfully harness the power of digital technologies gain a significant competitive advantage, not only in terms of cost savings and operational efficiency but also in their ability to deliver innovative products and services that meet the evolving needs of customers.